
Designated as one of the WOAH Reference Laboratory for Japanese encephalitis at the 81th WOAH General Session in May 2013.
Dr. Dong-Kun Yang
[Animal and Plant Quarantine Agency]
Viral Disease Division
[Animal and Plant Quarantine Agency]
Samples are submitted from provincial and private laboratories throughout Korea. APQA routinely conducts virus isolation from the submitted samples by using Vero cell lines (ATCC-81 in the American Type Culture Collection: ATCC) according to the Manual of Diagnostic Tests and Vaccines for Terrestrial Animals, WOAH at a bio-safety level (BSL) II plus facility located at the rabies laboratory. These samples include brain and aborted fetus obtained from swine and horses. During the recent three-year period, the rabies laboratory of the APQA has tested a lot of samples for virus isolation using Vero cell lines. Diagnostic tests used for virus identification include indirect fluorescent antibody test (FA), virus isolation, and reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR). Vero cells were cultured in α-MEM supplemented with antibiotics (100 IU/ml penicillin, 10 ㎍/㎖ streptomycin and 0.25 ㎍/㎖ amphotericin B) and 10% heat-inactivated fetal bovine serum (FBS: Gibco BRL). The cell culture was performed in 24 well plates at 37℃ under 5% CO2 incubator. About 10% brain homogenate or fetal fluid materials were centrifuged at 8,000rpm for 5min. The supernatant was filtered through 0.45㎛ membrane filter (Milipore) and 100 ml of filtrate was inoculated into monolayer of cells and followed by incubation at 37℃ for 1 hr. The inoculated aliquots were discarded and the cells were filled with fresh medium. The cells were screened for cytopathic effects (CPE) for 5 days and then the supernatants were removed and fixed with 80% chilled acetone for 15 min. For the staining of the cells, the cells were reacted with specific monoclonal antibody of JE for 45 min, and then stained with FITC conjugated goat anti-mouse IgG+IgM. After washing in PBS, the cells were examined by fluorescence microscopy (Nikon, Japan).
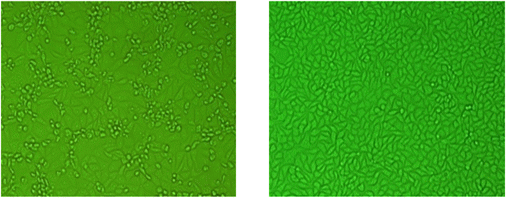
Fig. 1 Virus identification of JEV in Vero cells. Vero cells are routinely used at the JEV research laboratory of APQA for isolation and identification of JEV (Journal of Veterinary Science, Yang DK etal.2004).
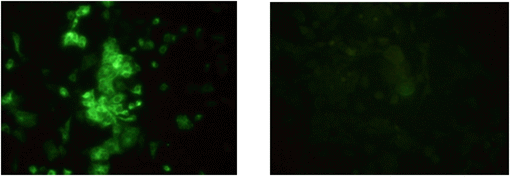
Fig. 2 Immunofluorescence staining of infected cells with JEV. Fluorescence was found in the cytoplasm. (Journal of Veterinary Science, Yang DK etal.2004).
In order to identify virus particles in the cell infected with JEV, the cells were harvested using a rubber policeman at 72 hr post-inoculation of the solate. After centrifugation at 1,500 rpm for 10 min, cell pellets were fixed with 2.5% glutaraldehyde in phosphate buffered saline (PBS) at 4℃ for 2.5 hr and post-fixed with 1% osmium tetroxide in PBS at 4 for 2 hr. After dehydration in a graded series of ethanol and propylene oxide, the cells were embedded in spur resin. Ultrathin sections were made and stained with uranyl acetate and lead citrate, and were observed under a Hitach 7100 electron microscope (Hitach, Japan).
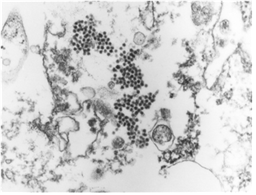
Fig. 3 JEV particles in cytoplasm of Vero cell infected with KV1899 strain. (J Vet Sci, Yang DK et. al, 2004).
Viral RNA is extracted from brain samples using an RNA extraction kit (Qiagen, Hilden, Germany) according to the manufacturer’s instructions. The extracted RNA is eluted in 50 μl of RNase- and DNase-free water. RT-PCR is carried out for the detection of RABV genomic sequences using specific primer set (JENDF and JENDR) that amplify the E gene of JEV. The primer set is listed in Table 1. The RT-PCR was performed in a reaction mixture containing 5 ml of denatured RNA, 1 ml of each primer (50 pmol), 5 ml of 5´ buffer (12.5 mM MgCl2),1ml of dNTP mix, 1 ml of enzyme mix (reverse transcriptase and Taqpolymerase),and11ml of distilled water (Qiagen, Hilden, Germany). The cycling profile is as follows: cDNA synthesis at 42°C for 30 min, followed by 45 cycles of 95°C for 15 sec, 55°C for 15 sec, and 72°C for 15 sec, with a final extension at 72°C for 5 min. The RT-PCR products are visualized using electrophoresis on 1.8% agarose gels containing ethidium bromide. The rabies research laboratory routinely performs RT-PCR using one step RT PCR kit to determine whether samples contain JEV. Currently, the RT-PCR kit is also routinely used for rapid detection of JEV by provincial diagnostic laboratories as supplementary diagnostic method. During the recent three-year period, the rabies research laboratory has performed RT-PCR assay for approximately 100 samples.
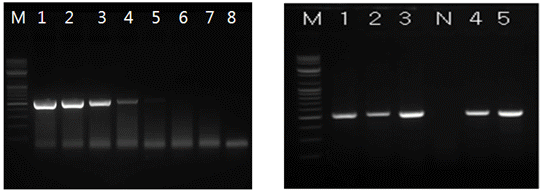
Fig. 4 Reverse-transcription polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) assay for virus identification. The detection limit of RT-PCR was found to be 25 TCID50/ml.
Table 1 List of the oligonucleotide primers used for RT-PCR of the JEV
| Primer | Nucleotide sequences (5'-3') | Sense | JEV gene |
Size of amplicon (bp) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JENDF | GCGTCTCAAGCAGCAAAGTT | + | E | 565 |
| JENDR | GTCATGTCGGTTTAAACTCGCGAC | - |
Mouse inoculation tests are performed according to the method of For this purpose, a 20%brain suspension or isolated virus were prepared and 0.03 ml is inoculated intracerebrally in 6 4 young white Balb/C mice (3–4 days old) with 2–3 g of weight. The animals are checked daily for 10 days after inoculation for typical nervous symptoms, such as emaciation, tremors, lack of coordination, paralysis and death. The mean survival time of the inoculated mice is defined as the mean time after inoculation between the day of the first appearance of clinical signs and the day of death.
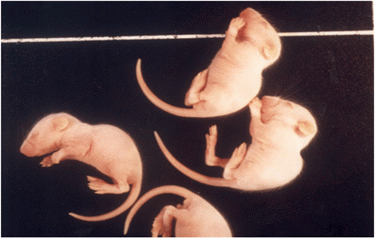
Fig. 5 Animal experiment for isolating JEV isolates. Intracerebral experiment using specific pathogen free mice is one of methods used for isolating JEV isolates. All experiments are performed in BL 3 laboratory equipped with the animal experimental facilities (J Vet Sci, Yang DK et. al, 2004).
HA test to check HA titer of concentrated JEV antigen was performed in 96-well microplates, using slightly modified standard methods. In short, 50 uL of concentrated antigen was diluted with 0.4% borate saline solution. After dilution, 50 uL of 0.33% goose erythrocytes were added, and the microplates were incubated at room temperature for 30 min. The HA titer was expressed as the reciprocal of the highest dilution of antigen showing complete hemagglutination.
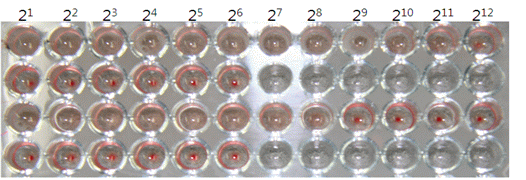
Fig. 6 HA titer of JEV antigen obtained from mice brain. (OJVM, Yang DK et al. 2012).
The APQA provides technical training for provincial diagnostic laboratories on the use and analysis of serological tests. In the Republic of Korea, forty three diagnostic laboratories routinely perform serological tests for the serological monitoring against JEV. Serological tests include hemagglutination inhibition (HI), virus neutralization test (VN) and plaque reduction inhibition test (PRNT). Diagnostic laboratories have serologically tested approximately 9000 pigs annually, including sows and fattening pigs. The data for the serological test results of the diagnostic laboratories are sent to the APQA for further analysis. The rabies laboratory has routinely tested serum samples from swine and horse as part of a diagnostic service, assessment of vaccination on animals and research projects for JE.
The sera were treated in round bottom microplates (96-well). To remove non-specific inhibitors, 10 ml of serum and 50 ml of 4% bovine albumin were mixed with 40 ml of 25% kaolin (Sigma, USA) and incubated for 30 min. After pipetting, the kaolin was removed by centrifugation at 3,600 rpm for 15 min in a microcentrofuge. The resultant clear supernatant was mixed with 5 ml of packed goose erythrocytes to remove any natural agglutinins. After incubation for 1 h at 37°C, the treated serum was separated from the goose erythrocytes by centrifugation. For the HI test, four to eight HA units of JEV (in 25 ml) were added to 25 ml of treated serum. After incubation for 1 h at 37°C, 50 ml of 0.33% goose erythrocytes were added, and the microplates were incubated at 37°C for 30 min. The HI titer was expressed as the reciprocal of the highest dilution of serum showing complete inhibition of hemagglutination. An HI titer of 1:10 or higher was considered positive.
Fig. 7 HI kit for the detection of antibody against JEV. The technical skill to produce the kits was developed in the viral disease division of APQA and transferred to a company that has supplied the kits to regional diagnostic laboratories.
The VN test with the inactivated sera at 56℃ for 30min was performed in a 96-well microplates using Vero cells. Serial dilutions of the sera were mixed with an equal volume of JEV, KV1899 virus suspension containing 200 TCID50/0.1ml. After incubating the virus-serum mixture at 37℃ for 1h, the Vero cells were added to the mixture to a final cell count of 20,000 cells/well. The plates were incubated at 37℃ under 5% CO2 for 3days. Each well was examined microscopically for cytopathic effect(CPE) and the neutralization titers were expressed as the reciprocal of the final serum dilution that inhibited CPE completely of the cultures. The serum dilution ranged from 1:2 to 1:256, and antibody titers of ≥ 1:8 were considered positive.
PRNT was performed by using monolayers of Vero cells in 24-well plates seeded with 1 ml of 3×104 Vero cell suspension per well in minimum essential media(MEM:GibcoBRL) with 10% heat-inactivated fetal bovine serum(FBS), and 100units of penicillin and streptomycin(GibcoBRL). Cells were incubated for 2days at 37°C. Test serum wash eat in activated at 56°C for 30minutes. In a cleanbench, 2-fold dilutions of the test sera beginning with a 1:10 dilution (1:10;1:20;1:40;1:80;1:160and1:320) with KV1899 virus diluent(0.3ml/dilution) were made. Virus-serum mixture was inoculated(0.1ml per well) and absorbed for 1 hour at 37℃ at which point the inoculums were removed. Media for the first overlay consisted of 0.5 ml of 1.0% low-melting point agarose and MEM containing 10% heat-inactivated FBS. The second overlay contained 1.0% low-melting point agarose in MEM with neutral red. Plaques were counted at 2 days of the second overlay. Positive control wells (virus without sera) were established for each assay run to ensure infectivity of the cell monolayer (formation of > 25 plaques).
Fig. 9 Plaque assay and PRNT performed at the rabies laboratory.